
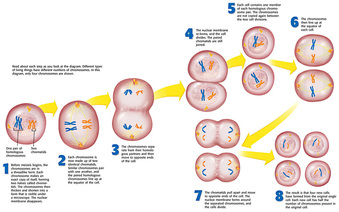
Motion results from a combination of kinetochore movement along The paired chromosomes separate at the kinetochores and move to opposite sides Will receive one copy of each chromosome. That in the next phase, when the chromosomes are separated, each new nucleus Line is referred to as the metaphase plate. Spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cell nucleus. Microtubules attachĪt the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. ProteinsĪttach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores.
The nuclear membrane dissolves, marking the beginning of prometaphase. Some fibersĬross the cell to form the mitotic spindle. To opposite ends of the cell and fibers extend from the centromeres. The cell may contain a pair of centrioles (or microtubule organizing centers in plants) both of which are organizational sites for microtubules.Ĭhromatin in the nucleus begins to condense and becomes visible in the light

Chromosomes are not clearly discerned in the nucleus, although a dark spot called the nucleolus may be visible. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Interphase is often included in discussions of mitosis, but interphase is technically not part of mitosis, but rather encompasses stages G1, S, and G2 of the cell cycle.
#PROPHASE VS INTERPHASE PLUS#
Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identicalĭaughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and To Cell Cycle & Mitosis > Tutorial The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial Mitosis What is (and is not) mitosis?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
